However, what about the remaining months of this year? Or if you spend most of your time inside? Should you be protecting your skin with sunscreen daily? In this section, we will discuss how the sun may damage your skin, why it is important to use sunscreen daily, and the advantages of applying sunscreen regardless of skin type.
What Are The Benefits Of Using Sunscreen?
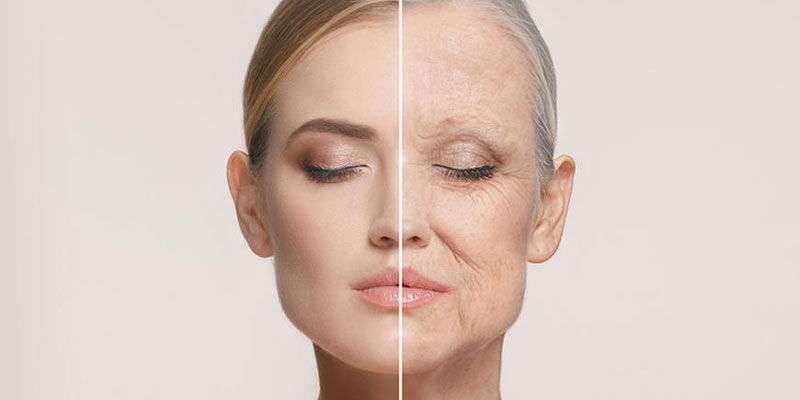
Being exposed to natural light and fresh air is beneficial to your health and may help you get vitamin D. But spending excessive time in the sun without proper protection might be harmful to your health. When you use sunscreen, you reduce your exposure to ultraviolet (UV) light, lowering your chance of developing skin cancer, the most frequent form of cancer in the United States. Using sunscreen may also prevent premature ageing of the Skin Care. It protects your skin against the damaging effects of ultraviolet (UV) radiation, including wrinkles, age spots, and a patchy complexion.
UV light
The sun generates a wide range of light beams, each of which has a unique wavelength. We can see some of them, which is referred to as visible light; however, we cannot view other forms of radiation, such as ultraviolet radiation. Your skin will react differently depending on the wavelength that is being emitted. Two of the three forms of ultraviolet light are harmful to human skin, and they are as follows:
- Exposure to ultraviolet A (UVA) rays has been linked to premature skin ageing.
- UVA and UVB radiation are harmful to the skin, even though their effects on the skin are distinct. Both may cause DNA damage in the skin, increasing the risk of skin cancer. The following are some more essential considerations about ultraviolet radiation:
- UV rays may be reflected off various materials, including water, snow, and sand, which can increase your exposure to the sun. Snow nearly doubles your UV exposure.
- UV rays may still pass through clouds. There is the potential for up to 80% of UV radiation to get through.
What Kind Of Protection Does Sunscreen Offer?
Sunscreen contains various active chemicals that block UV rays, reducing the amount of radiation your skin takes in. These components may be broken down into two primary categories:
- Chemical sunscreens have the same effect as a sponge; they take in the sun's rays. Avobenzone, oxybenzone, and octisalate are some of the components found in them.
- The sun's rays are deflected away from the skin by the reflective properties of physical sunscreens, which are also known as mineral sunscreens. Zinc oxide and titanium dioxide are both examples of these.

What exactly is SPF?
The sun protection factor, sometimes known as SPF, measures how well a product protects against sunburn caused by UVB radiation. If you were to use that sunscreen, the SPF number would inform you how long it would take for the sun's UVB rays to cause your skin to become irritated and red. If you were to wear sunscreen with a factor of 30, for instance, it would take you thirty times longer to burn than if you didn't use any sunscreen at all. SPF 50 blocks around 98% of the sun's rays, whereas SPF 100 blocks approximately 99% of them. The difference is not significant. No sunscreen blocks 100 percent of the sun.
How Many SPF Units Are Sufficient?
The minimal sun protection factor (SPF) that various medical organizations recommend varies from one group to the next. Detailed instructions may be found as follows:
- The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) and the World Health Organization recommend sunscreen with an SPF of 15 or higher.
- The Skin Cancer Foundation recommends using an SPF of 15 every day and an SPF of 30 or higher if you are in the sun.
- The American Cancer Society and the American Academy of Dermatology recommend sunscreen with an SPF of 30 or higher.
What If You Have Dark Skin?
Even while those with darker skin tones have some natural protection against the sun, the sun's ultraviolet radiation may nevertheless cause harm to those with lighter skin. Even if you don't burn easily in the sun or don't burn at all, sun damage may start to show up on your skin as uneven tone or pigmentation, which can be difficult to treat conditions such as melasma.

Alternatives To Sun Protection Products
The use of sunscreen is a method that is both risk-free and very effective in blocking the sun's damaging UV radiation. However, there are various techniques to protect oneself from the sun that does not entail using sunscreen, including the following:
- Keep cool in the shade (especially between 10 AM and 4 PM).
- Put on sunblock and caps with brims to protect yourself from the sun.
- When you go outdoors, be sure to bring an umbrella.
- Put on sunglasses that protect from UVA and UVB rays; this will keep your eyes and the skin around them safe.